❤️ Circulatory System
Introduction
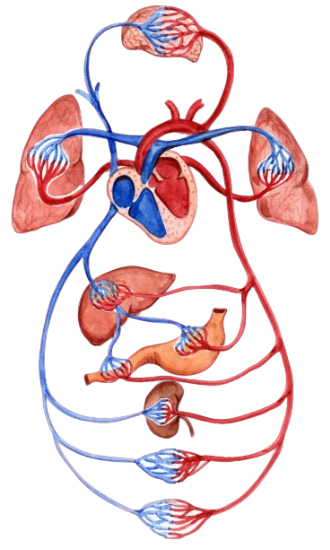
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, is responsible for transporting blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. It plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating body temperature, pH, and fluid balance.
This system consists of three main components: the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Functions of the Circulatory System
- Transportation – Delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues; removes waste products.
- Regulation – Maintains body temperature, pH levels, and fluid balance.
- Protection – White blood cells fight infections; platelets prevent blood loss.
Structure and Components
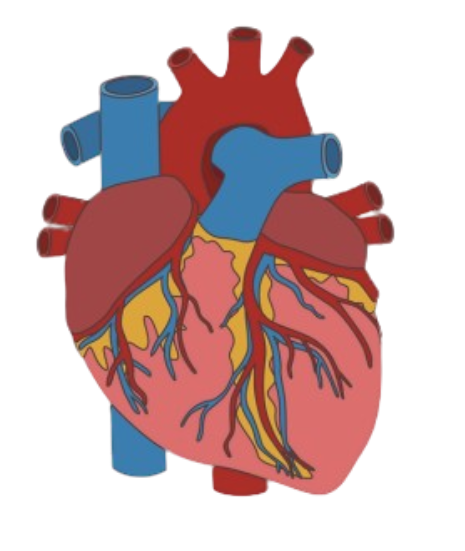
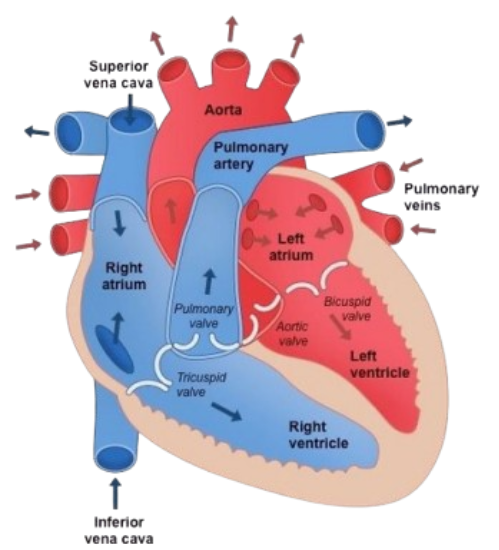
1. The Heart
A muscular organ that pumps blood through rhythmic contractions. It has four chambers:
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
The heart is divided by the septum and surrounded by a protective sac called the pericardium. Valves ensure one-way blood flow:
- Tricuspid valve (between right atrium and ventricle)
- Bicuspid/mitral valve (between left atrium and ventricle)
- Pulmonary and aortic valves (exiting heart)
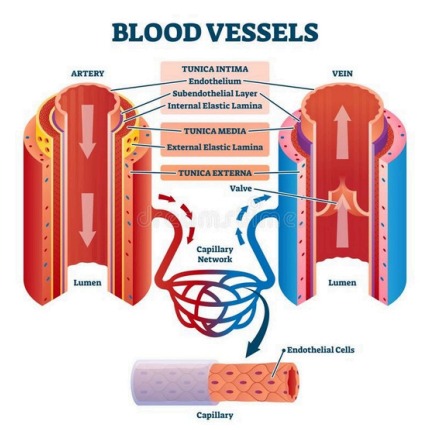
2. Blood Vessels
| Type | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Arteries | Carry blood away from the heart | Thick, elastic walls; carry oxygenated blood |
| Veins | Return blood to the heart | Thinner walls; have valves; carry deoxygenated blood |
| Capillaries | Connect arteries and veins | Thin-walled; site of gas and nutrient exchange |
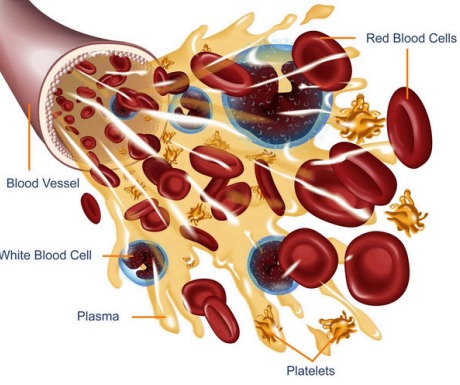
3. Blood
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Red Blood Cell (erythrocytes) | Carry oxygen using hemoglobin |
| White Blood Cell (leukocyte) | Defend the body against infection |
| Platelets (thrombocytes) | Help in blood clotting |
| Plasma | Liquid component that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste |
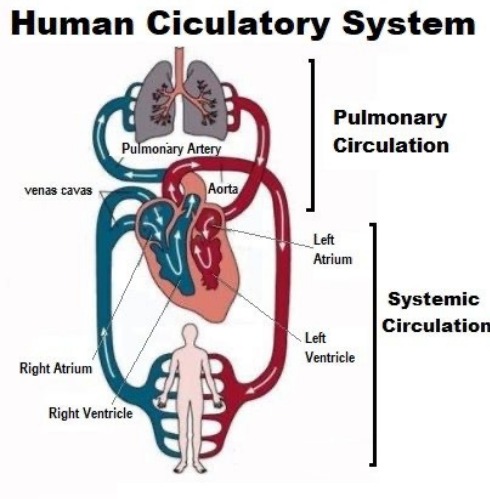
Circulatory Pathways
- Pulmonary Circulation – Right side of the heart ➔ lungs ➔ oxygenation ➔ returns to left side
- Systemic Circulation – Left side of the heart ➔ body tissues ➔ delivers oxygen/nutrients ➔ returns deoxygenated blood
Circulatory System Disorders
| Disorder | Description |
|---|---|
| Hypertension | High blood pressure; increases risk of stroke and heart attack |
| Atherosclerosis | Plaque buildup in arteries; restricts blood flow |
| Heart attack | Blockage of blood supply to the heart muscle |
| Stroke | Disruption of blood flow to the brain |
| Anemia | Reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood |
Keeping the Circulatory System Healthy
- Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Stay hydrated