🦴 Skeletal System
What is the Skeletal System?
The skeletal system is the internal framework of the human body. It is made up of bones, cartilage, and ligaments. This system supports the body, protects internal organs, and works with muscles to allow movement.
Main Functions of the Skeletal System
- Support – Provides structure and shape to the body.
- Protection – Shields important organs (e.g., skull protects the brain, ribs protect the heart and lungs).
- Movement – Bones work with muscles to produce movement.
- Mineral Storage – Stores calcium and phosphorus for later use.
- Blood Cell Production – Red and white blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
- Energy Storage – Yellow bone marrow stores fat as an energy reserve.
Structure of Bones
Bones are living tissues that are constantly growing and repairing. There are two main types of bone tissue:
- Compact bone – dense and strong, found on the outer layer of bones.
- Spongy bone – light and porous, found inside bones, especially at the ends.
Each bone has:
- Bone marrow – the soft tissue inside bones, where blood cells are produced.
- Periosteum – a membrane covering the outer surface of bones.
- Cartilage – a smooth, flexible tissue that cushions joints.
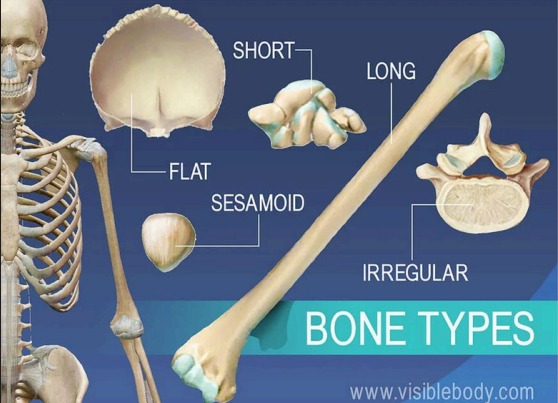
Types of Bones
| Bone type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Long bones | Longer than they are wide | Femur, humerus |
| Short bones | About equal in length and width | Carpals (wrist bones) |
| Flat bones | Thin and often curved | Skull, ribs, sternum |
| Irregular bones | Complex shapes | Vertebrae, facial bones |
| Sesamoid bones | Small and round, found in tendons | Patella (kneecap) |
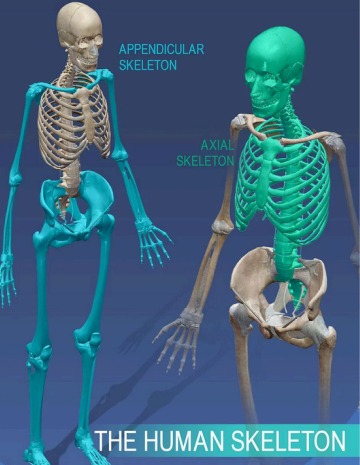
The Human Skeleton
The adult human skeleton has 206 bones. It is divided into two main parts:
- Axial Skeleton (80 bones)
- Skull
- Vertebral column (spine)
- Rib cage (ribs and sternum)
- Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones)
- Shoulder girdle and arms
- Pelvic girdle and legs
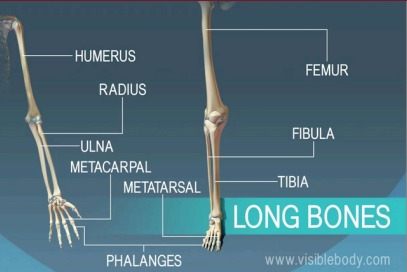
Major Bones to Know
| Bone | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cranium | Head | Protects the brain |
| Mandible | Jaw | Helps in chewing and speaking |
| Clavicle | Collarbone | Supports the shoulder |
| Scapula | Shoulder blade | Movement of the arms |
| Sternum | Chest | Protects heart and lungs |
| Humerus | Upper arm | Supports arm movement |
| Ulna | Forearm | Allows rotation and lifting |
| Pelvis | Hip area | Supports organs and body weight |
| Femur | Thigh | Longest and strongest bone |
| Patella | Knee | Protects the knee joint |
| Tibia | Lower leg | Supports weight and movement |
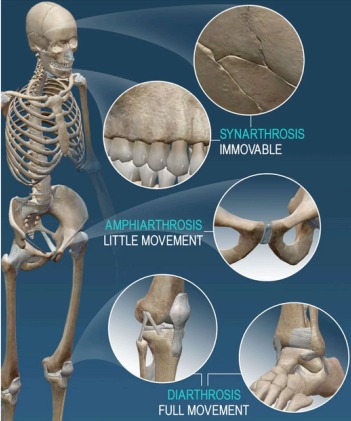
Joints and Movement
Joints are places where two or more bones meet. They allow movement and flexibility. There are three main types of joints:
- Immovable (fixed) – No movement (e.g., skull bones)
- Slightly movable – Limited movement (e.g., ribs, spine)
- Freely movable (synovial) – Wide range of movement (e.g., knee, elbow)
Types of synovial joints:
- Ball-and-socket (shoulder, hip)
- Hinge (elbow, knee)
- Pivot (neck)
- Gliding (wrist)
Interesting Facts:
- The femur can support up to 30 times the weight of your body!
- Babies are born with about 270 bones, but some fuse as they grow.
- The smallest bone is the stapes in the ear — only 3 mm long.