🍽️ Digestive System
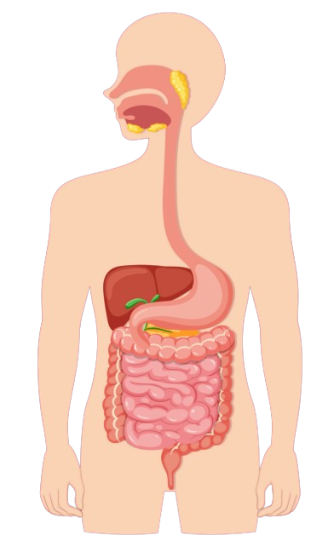
Introduction
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, absorbing those nutrients into the bloodstream, and eliminating waste products. It includes a complex group of organs that work together to convert food into energy and essential building blocks for the body.
Functions of the Digestive System
- Ingestion – Taking in food through the mouth
- Mechanical digestion – Physically breaking food into smaller pieces
- Chemical digestion – Enzymes and acids break down food molecules
- Absorption – Nutrients move into the bloodstream from the intestines
- Elimination – Removal of undigested waste as feces
Main Organs of the Digestive System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Mouth | Chewing (mechanical digestion); saliva begins chemical digestion |
| Esophagus | Transports food from mouth to stomach via peristalsis |
| Stomach | Churns and mixes food with gastric acid; begins protein digestion |
| Small intestine | Major site of digestion and nutrient absorption |
| Large intestine | Absorbs water; forms and stores feces |
| Rectum and anus | Expels feces from the body |
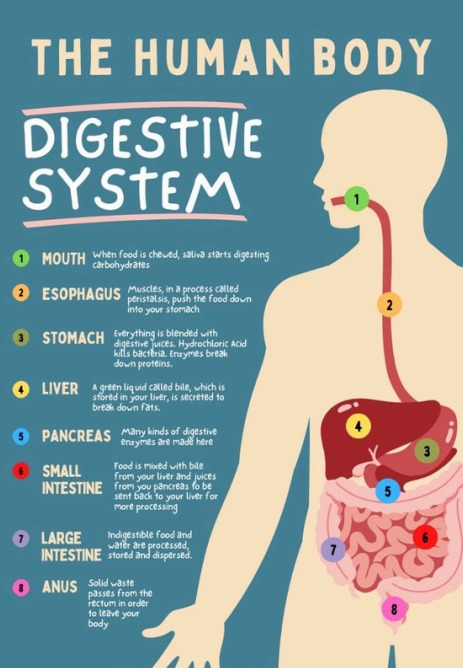
Digestive System Overview
Digestive Process Overview
- Mouth – Food is chewed and mixed with saliva (amylase begins starch digestion).
- Esophagus – Peristalsis pushes food toward the stomach.
- Stomach – Gastric juices break down proteins; food becomes chyme.
- Small Intestine – Enzymes complete digestion; nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Large Intestine – Water is absorbed; bacteria aid in final processing.
- Rectum/Anus – Waste is excreted.
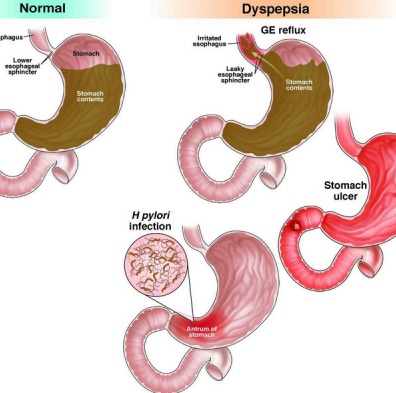
Common Digestive Disorders
| Disorder | Description |
|---|---|
| Acid reflux (GERD) | Stomach acid flows into the esophagus, causing heartburn |
| Constipation | Infrequent or difficult bowel movements |
| Diarrhea | Frequent, watery stools due to infection or irritation |
| Ulcers | Sores in the stomach lining caused by acid or bacteria |
| Lactose intolerance | Inability to digest lactose due to enzyme deficiency |