💪 Muscular System
Overview
The muscular system is responsible for body movement, posture maintenance, and internal organ function. It consists of over 600 muscles, making up approximately 40% of body mass.
Functions of the Muscular System
- Movement – Muscles contract to move bones and body parts.
- Posture and stability – Muscles keep the body upright and stable.
- Heat production – Muscle activity generates heat to maintain body temperature.
- Support for internal organs – Especially smooth and skeletal muscles.
- Circulation – Cardiac muscle pumps blood; smooth muscle controls vessel diameter.
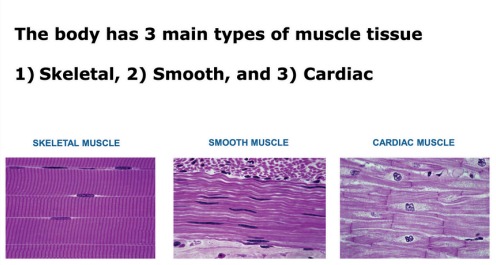
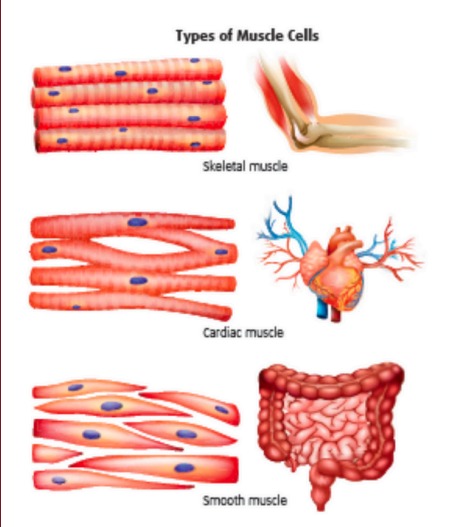
Types of Muscles
| Muscle Type | Location | Control | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skeletal | Attached to bones | Voluntary | Striated | Biceps, quadriceps |
| Cardiac | Heart only | Involuntary | Striated with intercalated discs | Myocardium |
| Smooth | Walls of hollow organs & vessels | Involuntary | Non-striated | Stomach, intestines |
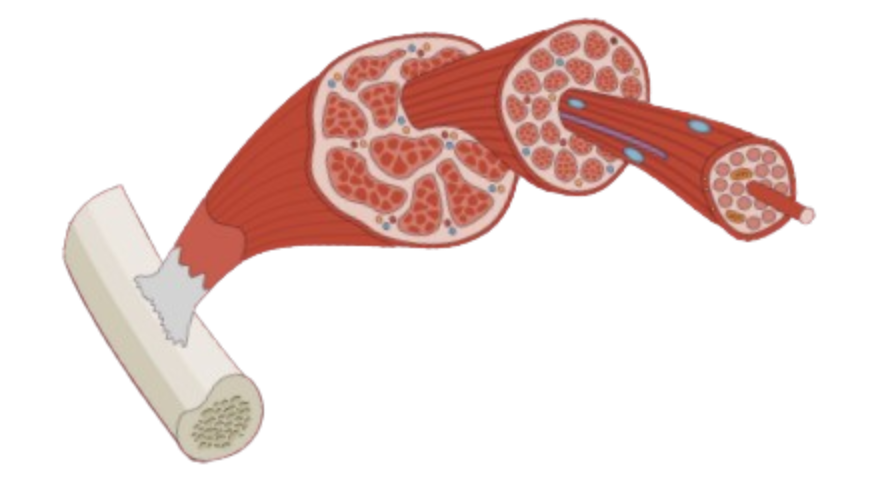
Muscle Anatomy
- Muscle fiber – a single muscle cell
- Fascicle – a bundle of muscle fibers
- Tendon – connective tissue attaching muscle to bone
- Myofibril – thread-like structures responsible for contraction
- Sarcomere – basic contractile unit of muscle
Muscles work in antagonistic pairs: when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes (e.g. biceps and triceps).
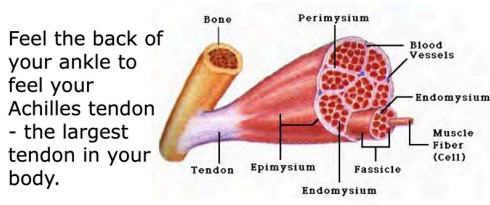
SKELETAL MUSCLES ATTACH TO BONES BY TENDONS(CONNECTIVE TISSUE) AND ENABLE MOVEMENT.
WE CAN CONTROL THEM. FOR EXAMPLE, MUSCLES OF LEGS, HANDS OR HEAD.
Muscle Structure and Contraction
Each skeletal muscle consists of bundles of muscle fibers, which contain smaller units called myofibrils. These myofibrils are composed of sarcomeres — the functional units of muscle contraction. Contraction occurs when actin and myosin filaments slide past each other using energy (ATP), regulated by signals from the nervous system and the release of calcium ions.
Key Terms:
- Tendon – Connects muscle to bone
- Ligament – Connects bone to bone
- Origin – Fixed attachment point of a muscle
- Insertion – Movable attachment point
Maintaining a Healthy Muscular System
- Regular physical activity (strength and endurance training)
- Adequate intake of protein, calcium, and hydration
- Proper posture and body mechanics
- Stretching and warm-ups before intense activity
- Avoidance of overuse and repetitive strain