👶 Reproductive System
Introduction
The reproductive system ensures the continuation of species by enabling humans to produce offspring. It includes both primary sex organs (gonads) and accessory structures. The male and female reproductive systems differ in structure and function but work together during reproduction.
In addition to reproduction, this system is responsible for hormonal regulation during puberty and adulthood.
Functions of the Reproductive System
- Produce gametes (sperm and eggs)
- Transport and nourish gametes
- Support fertilization
- Enable the development of a fetus (female system)
- Produce sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen, progesterone)

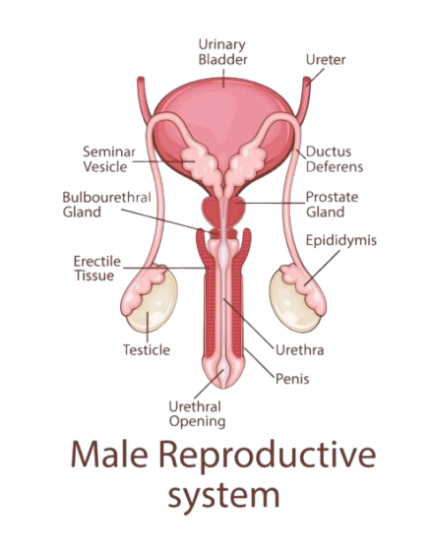
Мужская репродуктивная система
| Орган | Функция |
|---|---|
| Testes | Produce sperm and testosterone |
| Epididymis | Stores and matures sperm |
| Vas deferens | Transports sperm from testes to urethra |
| Seminal vesicles | Secrete fluid that nourishes sperm |
| Prostate gland | Produces fluid that helps sperm motility |
| Urethra | Carries semen (and urine) out of the body through the penis |
| Penis | External organ that delivers sperm |
- Testosterone – stimulates sperm production, male secondary sex characteristics.
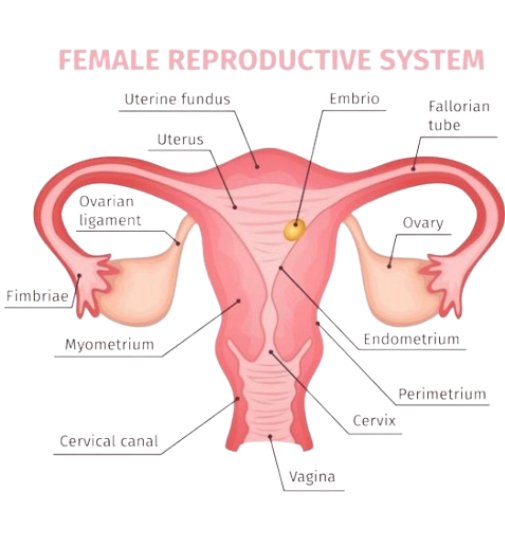
Female Reproductive System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Ovaries | Produce eggs (ova) and hormones (estrogen, progesterone) |
| Fallopian tubes | Transport eggs from ovary to uterus; site of fertilization |
| Uterus | Supports fetal development |
| Endometrium | Inner lining of uterus; thickens monthly and sheds if no pregnancy |
| Cervix | Lower part of uterus; opens into the vagina |
| Vagina | Receives sperm; birth canal |
- Estrogen – develops female characteristics, regulates menstrual cycle
- Progesterone – prepares uterus for pregnancy
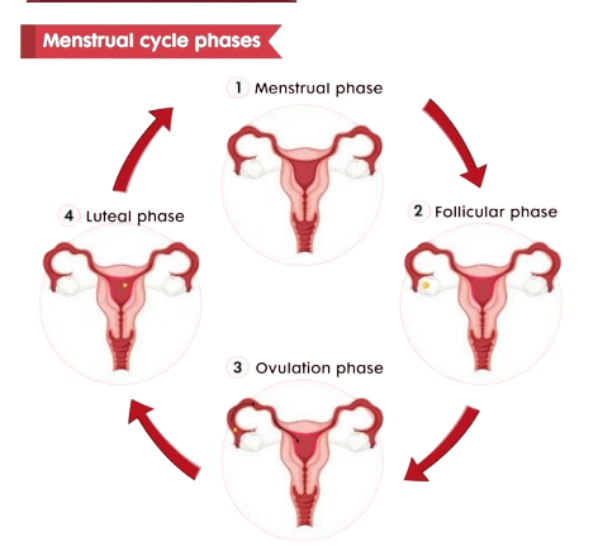
The Menstrual Cycle
A ~28-day cycle involving changes in the uterus and ovaries.
Controlled by hormones from the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries.
Ovulation occurs around day 14.
If fertilization does not occur, the endometrial lining is shed (menstruation).
Fertilization and Pregnancy
Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell unites with an egg cell in the fallopian tube.
The fertilized egg becomes a zygote, which implants into the uterine wall.
Development continues through stages: embryo → fetus → birth.
Puberty and Hormonal Changes
Puberty is the period when reproductive organs mature, triggered by hormonal changes:

Reproductive Health Tips
- Practice safe hygiene and sexual health
- Get regular medical check-ups
- Maintain hormonal balance with good nutrition
- Avoid stress, smoking, and alcohol abuse
- Educate adolescents about puberty and body changes
