🫁 Respiratory System
Introduction
The respiratory system is responsible for the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide—gases essential for cellular respiration and energy production. This system ensures the continuous exchange of gases between the body and the environment, allowing cells to function properly and maintain life.
Functions of the Respiratory System
- Gas exchange – Supplies oxygen to the bloodstream and removes carbon dioxide.
- Speech production – Air passes through the vocal cords in the larynx.
- Olfaction – Sense of smell through receptors in the nasal cavity.
- Regulation of blood pH – Helps control acidity through CO2 levels.
- Protection – Traps pathogens and dust with mucus and cilia.
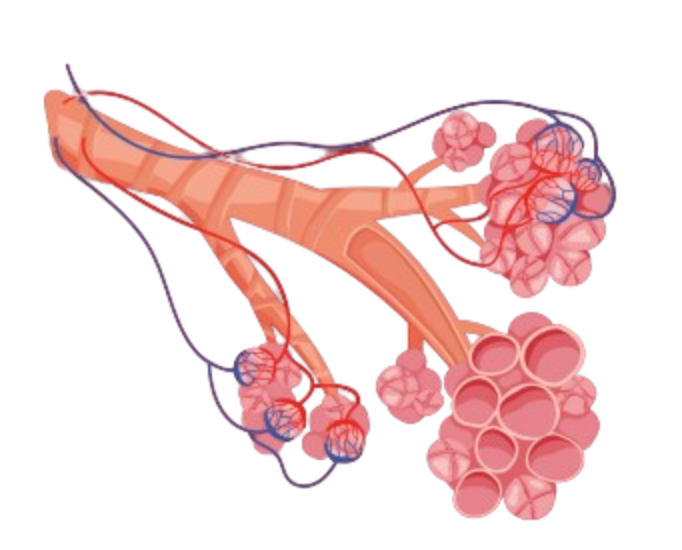
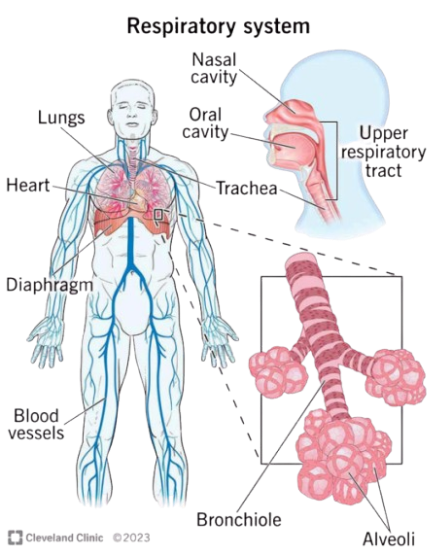
Organs of the Respiratory System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Nose/Nasal cavity | Warms, moistens, and filters air; detects odors |
| Pharynx | Passageway for air and food |
| Larynx | Contains vocal cords; routes air into the trachea |
| Trachea | Windpipe that carries air to the bronchi |
| Bronchi | Two large branches leading to each lung |
| Bronchioles | Smaller branches distributing air within the lungs |
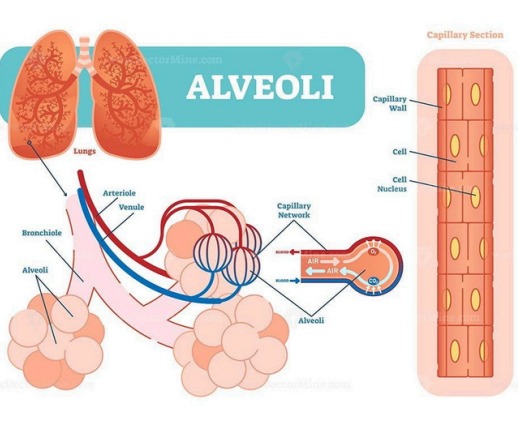
| Alveoli | Tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs |
| Lungs | Main organs of respiration |
| Diaphragm | Muscle that contracts to pull air into the lungs |
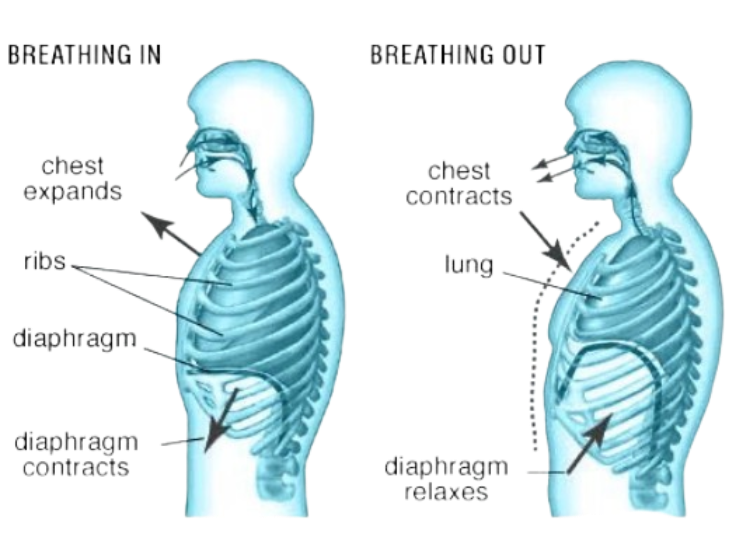
The Process of Breathing
Inhalation (Inspiration):
- Diaphragm contracts and flattens
- Chest cavity expands
- Air pressure drops; air flows into lungs
Exhalation (Expiration):
- Diaphragm relaxes
- Chest cavity returns to normal
- Air is pushed out
Gas Exchange in the Alveoli
- Oxygen diffuses from alveoli into capillaries
- Carbon dioxide diffuses from capillaries into alveoli
- Это происходит путем диффузии через альвеолярно-капиллярную мембрану
Каждый легкое содержит примерно 300 миллионов альвеол, что максимизирует площадь поверхности для газообмена.
Common Respiratory Disorders
| Disorder | Description |
|---|---|
| Asthma | Inflammation and narrowing of airways |
| Bronchitis | Inflammation of bronchial tubes, often from infection or smoking |
| Pneumonia | Infection causing fluid buildup in alveoli |
| Emphysema | Disruption of blood flow to the brain |
| Lung cancer | Uncontrolled cell growth in lung tissue |
Keeping the Respiratory System Healthy
- Avoid smoking and exposure to pollutants
- Exercise regularly to strengthen lung capacity
- Stay hydrated to keep mucus thin and effective
- Practice good hygiene to prevent respiratory infections
- Breathe through the nose to filter and warm the air