🫘 Excretory (Urinary) System
Introduction
The excretory system is responsible for removing waste products and maintaining the body’s internal balance of water, salts, and pH. The urinary system is the primary component of excretion, filtering blood to form urine and eliminate toxic substances from the body.
Functions of the Excretory System
- Filtration – Removes waste products from the blood
- Urine formation – Produces and excretes urine
- Regulation – Maintains fluid and electrolyte balance
- Homeostasis – Helps control blood pressure and pH
- Detoxification – Eliminates excess ions, toxins, and drugs
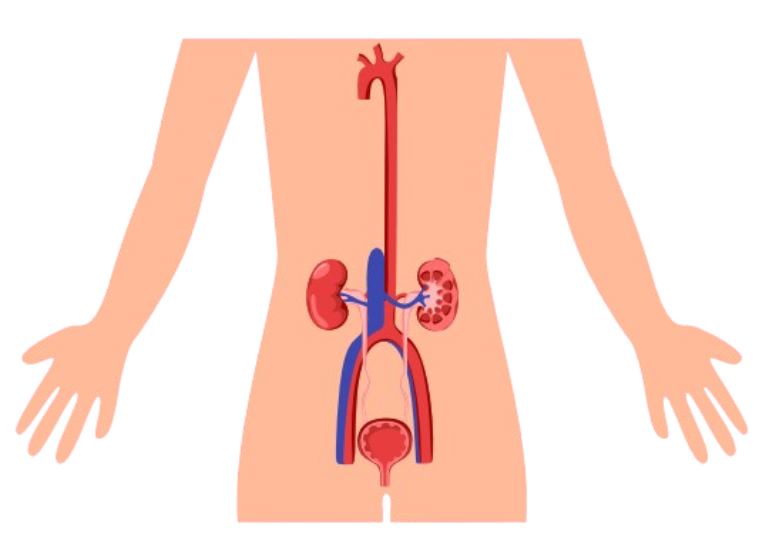
Organs of the Urinary System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Kidneys | Filter blood, remove waste, regulate water and salt balance |
| Ureters | Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder |
| Urinary bladder | Stores urine until excretion |
| Urethra | Carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body |
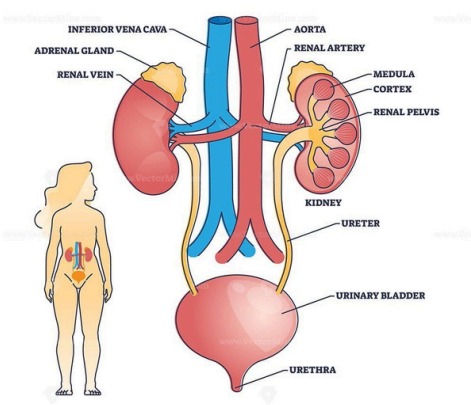
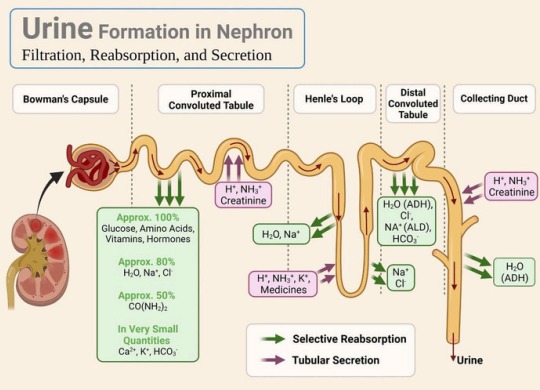
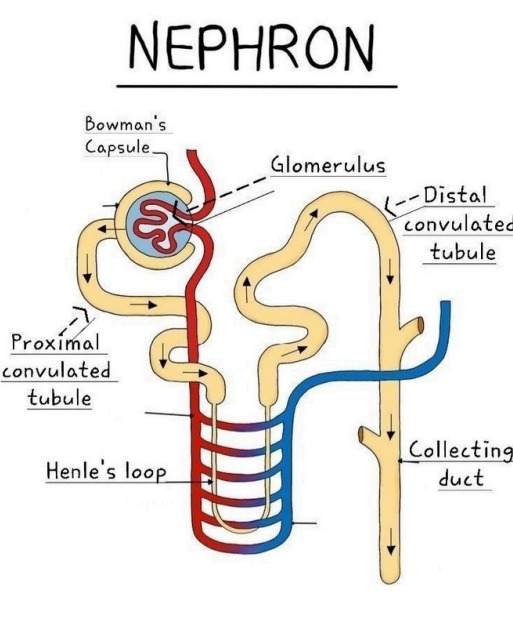
Structure and Function of the Kidneys
Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons, the functional units that filter blood and form urine. The process involves:
- Filtration – Blood is filtered in the glomerulus
- Reabsorption – Useful substances (e.g. water, glucose) are reabsorbed into the blood
- Secretion – Additional waste and ions are secreted into the tubule
- Excretion – Final urine is collected in the renal pelvis and moves to the ureter