🛡️ Immune and Lymphatic Systems

Introduction
The immune system protects the body from pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and harmful substances. Closely connected to it, the lymphatic system helps in maintaining fluid balance and transporting immune cells. Together, these systems defend the body and maintain internal health.
Functions of the Immune and Lymphatic Systems
- Protect the body from infections and disease
- Identify and destroy foreign substances (antigens)
- Remove dead cells and cellular waste
- Produce and circulate lymphocytes
- Maintain fluid balance in tissues

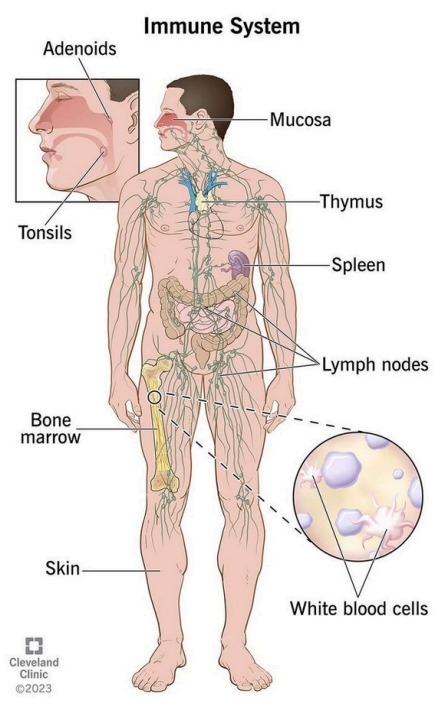
Components of the Immune System
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| White blood cells (leukocytes) | Identify and destroy pathogens |
| Lymphocytes (T-cells, B-cells) | Specialized WBCs that target specific threats |
| Antibodies | Proteins that neutralize or destroy foreign invaders |
| Bone marrow | Produces blood cells, including immune cells |
| Thymus | Site where T-cells mature |
| Spleen | Filters blood, removes old cells, stores white blood cells |
| Lymph nodes | Filter lymph and trap pathogens |
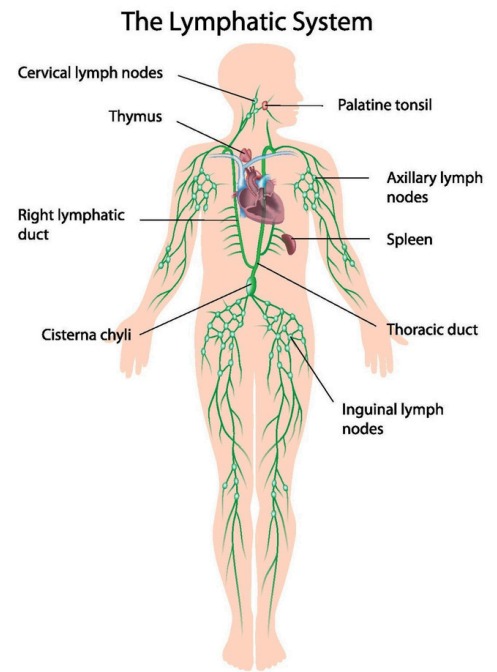
Components of the Lymphatic System
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Lymph | Clear fluid that transports white blood cells and waste |
| Lymph vessel | Network of tubes carrying lymph throughout the body |
| Lymph nodes | Small structures that filter lymph and house immune cells |
| Spleen | Filters blood and supports immune response |
| Thymus | Produces and trains T-cells |
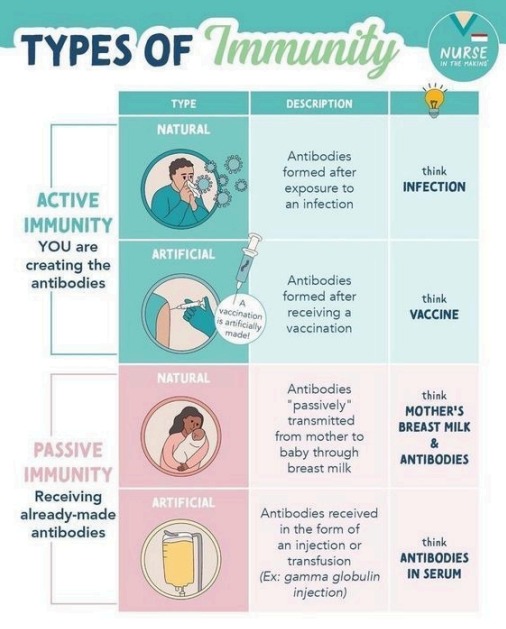
Types of Immunity
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Innate immunity | Present at birth; immediate, non-specific defense |
| Adaptive immunity | Acquired after exposure; specific and long-lasting (e.g. vaccines) |
| Active immunity | Body produces its own antibodies (infection or vaccination) |
| Passive immunity | Antibodies are received from another source (e.g. mother to baby via breastmilk) |

Immune Response Process
- Detection – Antigen is recognized by immune cells
- Activation – T-cells and B-cells respond
- Antibody production – B-cells produce specific antibodies
- Destruction – Antibodies and cells neutralize the threat
- Memory formation – Body remembers the antigen for future protection
