⚗️ Endocrine System
Introduction
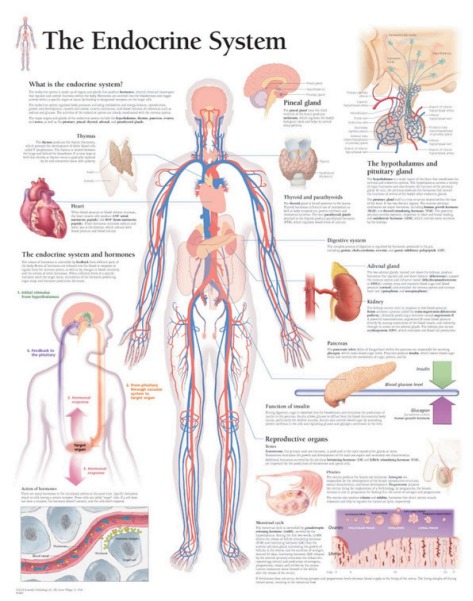
The endocrine system is a regulatory system comprised of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones control and coordinate many essential body functions such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, mood, and homeostasis.
Unlike the nervous system, which works through electrical impulses and rapid responses, the endocrine system regulates the body over longer periods using chemical messengers.
Functions of the Endocrine System
- Regulates metabolism and energy balance
- Controls growth and development
- Manages reproductive processes
- Maintains homeostasis (fluid balance, blood pressure, calcium levels)
- Responds to stress and emotional states
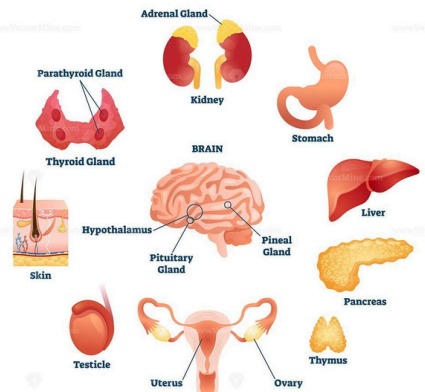
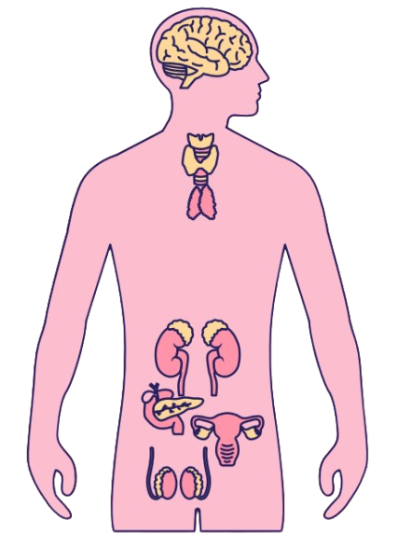
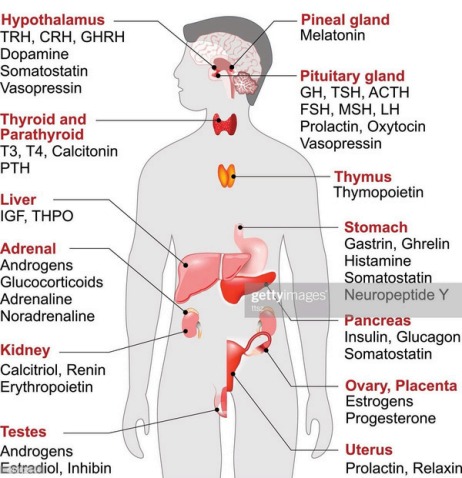
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones
| Gland | Location | Hormones Secreted | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pituitary gland | Brain (base) | Growth hormone (GH), TSH, LH, FSH | Master gland; regulates other glands |
| Hypothalamus | Brain (above pituitary) | Releasing/inhibiting hormones | Connects nervous and endocrine systems |
| Thyroid gland | Neck | Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3) | Regulates metabolism, heart rate, and temperature |
| Parathyroid glands | Behind thyroid | Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Regulates calcium levels |
| Adrenal glands | On top of kidneys | Adrenaline, cortisol, aldosterone | Controls stress response, metabolism, salt-water balance |
| Pancreas | Abdomen | Insulin, glucagon | Regulates blood glucose |
| Ovaries (females) | Pelvis | Estrogen, progesterone | Controls female reproductive system |
| Testes | Scrotum | Testosterone | Controls male reproductive system |
How Hormones Work
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to target organs or cells. They bind to specific receptors, triggering a specific response. Hormone release is usually controlled by negative feedback mechanisms.
Example:
- When blood sugar is high » pancreas releases insulin » blood sugar decreases
- When blood sugar is low » pancreas releases glucagon » blood sugar increases
Maintaining Endocrine Health
- Maintain a balanced diet with adequate iodine and nutrients
- Get regular physical activity
- Manage stress levels
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Regular health checkups, especially for blood sugar and thyroid function