🧠 Nervous System
Introduction
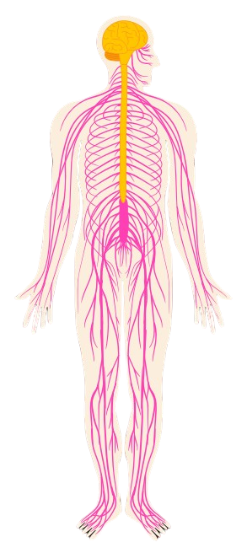
The nervous system is the body's control and communication network. It coordinates actions, thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions by transmitting electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. As one of the most complex and vital systems, it plays a central role in sensation, integration, and response.
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system is responsible for three key functions:
- Sensory Input – Detects changes inside and outside the body (e.g. temperature, pain, light).
- Integration – Processes and interprets sensory input and makes decisions.
- Motor Output – Sends commands to muscles and glands to respond (e.g. move hand, release hormones).
Divisions of the Nervous System
| Division | Description |
|---|---|
| Central Nervous System (CNS) | Brain and spinal cord; processes information and coordinates activity |
| Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) | Nerves outside CNS; carries messages between the body and the CNS |
PNS: Further Divisions
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is further divided into:
- Somatic Nervous System – controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
- Autonomic Nervous System – manages involuntary functions (heartbeat, digestion, etc.).
The Autonomic Nervous System includes two divisions:
- Sympathetic Division – "fight or flight" response (activates the body in stressful situations).
- Parasympathetic Division – "rest and digest" response (relaxation, recovery, digestion).
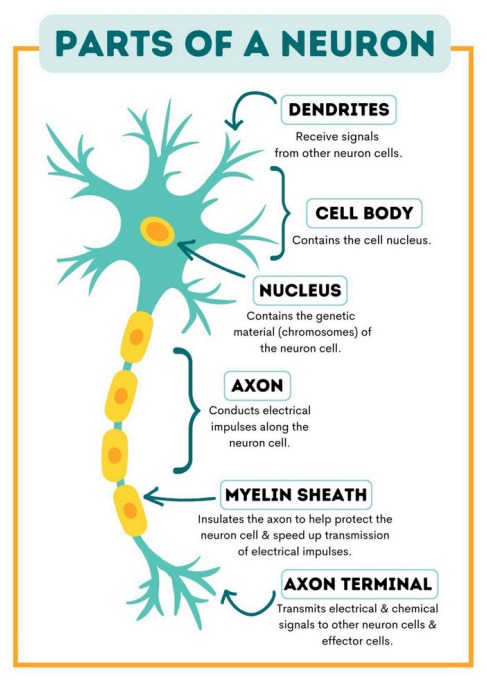
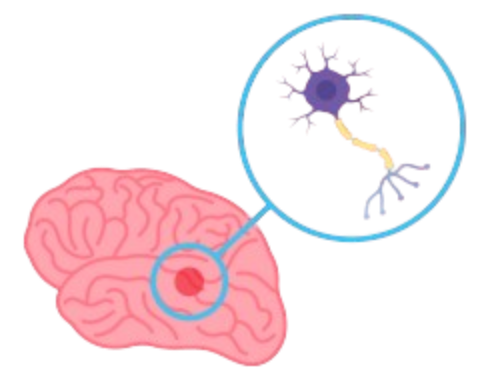
Neuron Structure
Neurons are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system.
A typical neuron consists of:
- Cell Body (Soma) – contains the nucleus
- Dendrites – receive signals from other neurons
- Axon – transmits signals away from the cell body
- Myelin Sheath – insulates the axon and speeds up signal transmission
- Synapse – the contact point between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released
There are three main types of neurons:
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensory Neurons | Transmit signals from receptors to the CNS |
| Motor Neurons | Transmit commands from the CNS to muscles/glands |
| Interneurons | Connect sensory and motor neurons (within the CNS) |
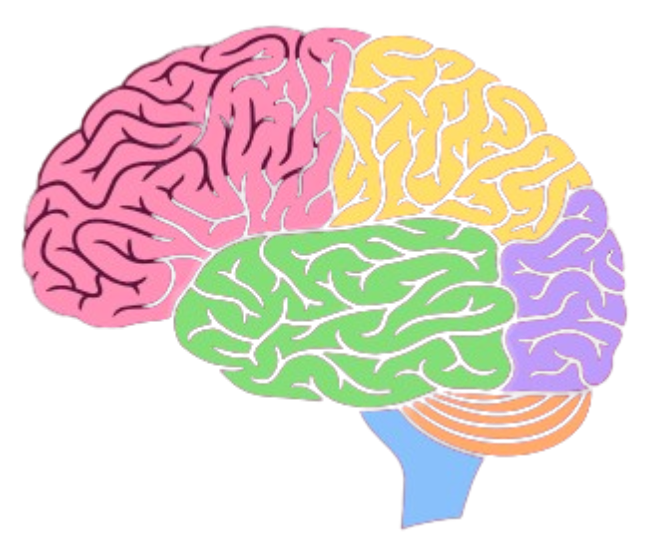
The Brain and Its Regions
The brain is the control center of the body. It is divided into major regions:
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Controls thinking, memory, movement, and senses |
| Cerebellum | Coordinates movement and balance |
| Brainstem | Controls breathing, heart rate, and digestion |
| Hypothalamus | Regulates body temperature, hunger, and emotions |
| Medulla oblongata | Manages vital involuntary functions like respiration and heartbeat |
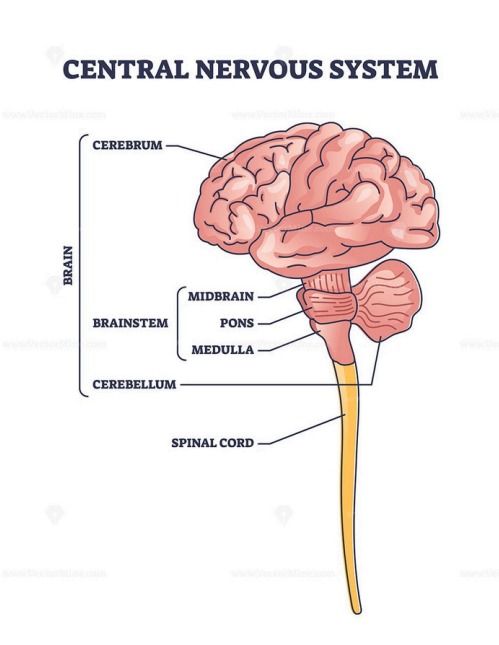
The Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin bundle of nerve tissue that extends from the brainstem down the back. It:
- Transmits messages between the brain and body
- Is protected by the vertebrae
- Has 31 pairs of spinal nerves
Common Nervous System Disorders
| Disorder | Description |
|---|---|
| Parkinson’s disease | Affects movement; caused by dopamine deficiency |
| Alzheimer’s disease | Progressive memory loss and confusion |
| Epilepsy | Recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical brain activity |
| Multiple sclerosis | Immune system attacks the myelin sheath |
| Stroke | Brain damage due to interrupted blood flow |
Keeping the Nervous System Healthy
- Get adequate sleep (7–9 hours per night)
- Eat brain-friendly foods (omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, whole grains)
- Avoid drugs, alcohol, and smoking
- Practice mental activities (reading, puzzles)
- Stay physically active to support blood flow to the brain